Metrology

Photo by Bornil Amin on Unsplash

Wrapped snugly in a custom container, seven carefully chosen materials left Earth on Aug. 24, 2025, traveling at 17,500 mph. Nestled at the top of a Falcon 9 rocket, house dust, freeze-dried human liver, and cholesterol joined four other scientific specimens to travel to the International Space…

In an emergency, knowing exactly where a first responder is can mean the difference between life and death. When a firefighter in a burning building fails to check in, how does the commander know where to look for them?
Public safety agencies face daily challenges in finding first…

Thickness is one of the most frequently measured dimensions, and one that’s very easy to understand. So, you might think that someone would come up with a one-style-fits-all measurement approach that’s good for just about every kind of thickness application. But it just isn’t so.
…

The Pantone Color of the Year 2026, PANTONE 11-4201 Cloud Dancer, is described as an airy, billowy white that opens space for creativity, quiet reflection, and calm. A white that is both warm and cool, its serene presence symbolizes the need for clarity in a noisy world.
As soon…
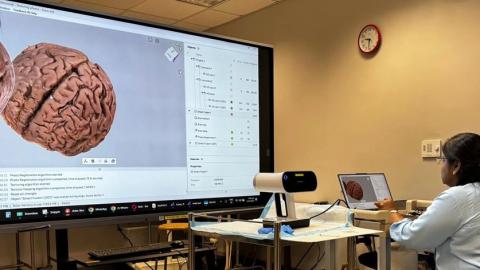
In the medical field, 3D technology is fast becoming indispensable. Whether used for educating patients ahead of surgeries or teaching students how to do these operations, anatomy models, both 3D printed and digital, offer an ideal solution for visualization ahead of time.
One of…

Measurement, in its most basic form, is about comparing the thing you want to measure with a reference. To measure the length of a table, you compare it to a tape measure. To measure flour for a birthday cake, you compare it to a measuring cup. Better references mean better measurements.
…Featured Video
