In previous articles we have explored what differential privacy is, how it works, and how to answer questions about data in ways that protect privacy. All of the algorithms we’ve discussed have been demonstrated via mathematical proof to be effective for protecting privacy. However, when translating these algorithms from paper to code, it’s possible to introduce bugs in the resulting software, which can result in failure to protect privacy. Here, we'll explore what these bugs typically look like, why it is so hard to detect them, and approaches to software assurance that can ensure your implementation is free from bugs.
|
ADVERTISEMENT |
What does a privacy bug look like?
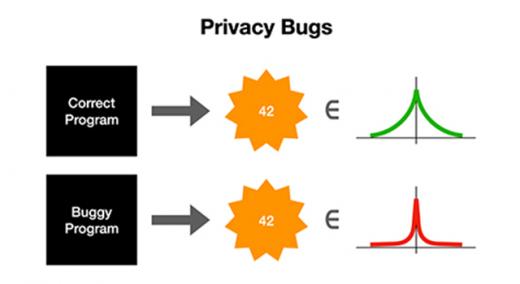
What does a “privacy bug” look like when implementing differentially private algorithms? Remember that the central idea of differential privacy is to add noise to data analysis results to protect privacy. When a certain quantity of noise is added, a certain quantity of privacy is achieved. Privacy bugs happen when too little noise is added, resulting in too little achieved privacy, or when too much noise is added, resulting in too much degradation of the result’s accuracy.
…
Add new comment