(Paul Scherrer Institute: Villigen, Switzerland) -- A novel nano-tomography method developed by a team of researchers from the Technische Universität München (TUM), the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI), and the ETH Zurich opens the door to computed tomography (CT) examinations of minute structures at nanometer resolutions. The new method makes possible, for example, 3-D internal imaging of fragile bone structures. The first nano-CT images generated with this procedure was published in the journal Nature on Sept. 23. This new technique will facilitate advances in life sciences and materials sciences.
|
ADVERTISEMENT |
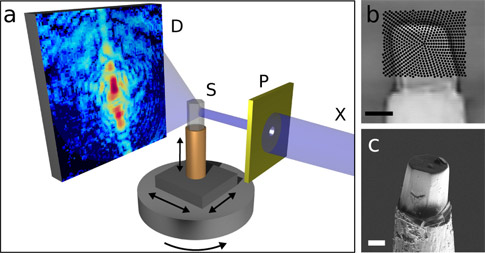
Schematic of the new nano-computed tomography (CT) method: The sample is scanned with an X-ray beam while the detector records a diffraction pattern for every beam position. The sample is then turned around its axis and scanned again, until a complete set of data is gathered for every angle. A high-resolution 3-D image of the sample is then computed from the hundreds of thousands of diffraction patterns by means of specially developed image reconstruction algorithms.
…
Add new comment