Do you still insist on asking, “Which chart do I use for which situation?”
|
ADVERTISEMENT |
I’ve seen many flowcharts in books to help you answer this question. They’re all some variation of this:
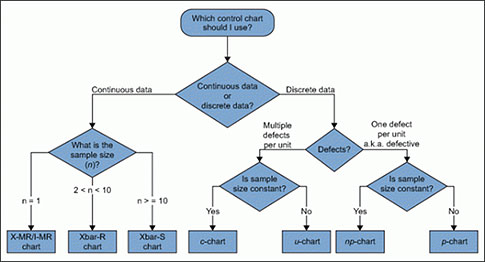
I find them far too confusing for the average user and have never taught this in my work. Besides, you get no credit for choosing the technically correct chart or computing the right numbers—only for taking the right action.
Your ‘Swiss Army knife’
For any initial chart for process assessment, the data should be in its naturally occurring time sequence, preferably as a run chart. Next, the control chart of choice with which to start is virtually almost always the I-chart (individuals chart), which uses the moving range (MR) between consecutive points to determine its common-cause limits. The I-chart is the “Swiss Army knife” of control charts. As I have discovered time and time again, it usually approximates the “correct” chart under most conditions, and its use is easier to explain.
I can hear the chorus: “So, what are the conditions when it isn’t correct?”
…
Comments
I-MR Chart
Teaching charts
Ditto - I teach from a pre-done class and I make about a 1 minute comment about the rest that if the IMR chart doesn't work, there are other options. I agree with Davis' comment about generalization and would extrapolate to just about any industry outside of manufacturing, the sample size is 1.
Verifying Assumptions for Attribute charts
The notion that a typical user of control charts is able to verify the theoretical assumptions that Wheeler writes about in his books on charts for counts is just not realistic. With the XmR chart, you can skip all that since the limits are empirical. This allows you to get to work on the process right away.
Rich
Software or Brainware?
Most SPC software asks you to figure out which control chart to use before you select data.
This means that you have to mentally walk through a forest of decision trees to get a chart. You have to use your noggin--your brainware. For the expert this is easy; for the novice or occasional user this can be difficult.
The QI Macros for Excel asks you to select the data first. That way the Control Chart Wizard can analyze your data, run through the decision trees for you and choose the right chart.
So, do you want to keep using your brainware and worrying that you've made the right choice?
Or would you rather let your software help you get the right answer?
Add new comment