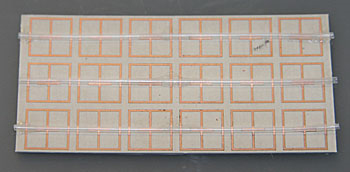
A metasurface or metafilm is a 2-D version of a metamaterial, popularized recently in technologies with seemingly unnatural properties, such as the illusion of invisibility. Metamaterials have special properties not found in nature, often because of a novel structure. NIST’s metasurface is a small piece of composite circuit board studded with metal patches in specific geometries and arrangements to create a structure that can reflect, store, or transmit energy (i.e., allow it to pass right through).
|
ADVERTISEMENT |
NIST researchers used purified water to tune the metasurface’s resonant frequency—i.e., the specific microwave frequency at which the surface can accumulate or store energy. They also calculated that the metasurface could concentrate electric field strength in localized areas, and thus might be used to heat fluids and promote microwave-assisted chemical or biochemical reactions.
…
Add new comment