You need to police yourselves," declared ISO secretary general Lawrence D. Eicher during his
opening speech at the 17th meeting of the International Standards Organization's Committee on Conformity Assessment. Speaking to certification bodies and the accreditation bodies that approve
them, he urged groups to start doing a better job of monitoring their communities to weed out malpractice and dishonest operators. Noting that the conformity assessment
community is facing a serious challenge caused by some certification bodies acting without integrity, Eicher expressed concern about improper certification practices. He suggested that all
conformity assessment professionals need to be concerned too if they want to avoid being seen as "charlatans." Although ISO itself doesn't audit companies, issue ISO
9000 certificates or control certification bodies, those bodies base their business on ISO standards and guides. "Therefore, when certification bodies act without integrity, many people
believe that it is ISO's fault," Eicher said. "We regularly receive complaints about certificates being awarded undeservedly to companies that have not been properly
audited, about certification bodies that offer to write the quality manual for the company and then sell them a certificate, or about others that claim to have been approved by ISO. No one at ISO
has ever approved such certification bodies." The meeting attracted more than 100 people from 35 countries and 16 international organizations in liaison with the Committee
on Conformity Assessment. CASCO develops standards and guides for conformity assessment and encourages best practice and consistency when products, services, systems, processes and materials need
to be evaluated against standards, regulations or other specifications. Learn more at the ISO Web site at www.iso.org. ISO Introduces Guidelines
for Food and Drink Industry The International Organization for Standardization has published guidelines for the food and drink industry for implementing quality management
systems based on ISO 9001:2000. The new standard, ISO 15161, Guidelines on the application of ISO 9001:2000 for the food and drink industry, is aimed at organizations involved
in all aspects of this industry sector, including sourcing, processing and packaging food and drink products. To assist the user, the requirements of ISO 9001:2000 are given in boxed text,
followed by guidance relevant to the user. "ISO 9001 focuses on customers' needs and expectations," say experts of ISO technical committee ISO/TC 34, Food products,
which developed ISO 15161. The introduction to the new guidelines states: "One of the most important customer expectations (and often one which is implicit rather than stated directly) is to
have safe food products. ISO 15161 allows an organization to integrate its quality management system with the implementation of food safety systems, such as HACCP (hazard analysis and critical
control point)." According to the committee's experts, application of HACCP within an ISO 9001:2000 quality management system can result in a food safety system that is
more effective than the application of either ISO 9001:2000 or HACCP alone. Links between the basic principles of HACCP and specific clauses of ISO 9001:2000 are shown in an annex. Additionally,
any other accepted food safety system can also be integrated with the quality management system. The guidelines can be purchased for about $70. To obtain a copy, contact any
national member institute or the ISO Central Secretariat sales@iso.org . 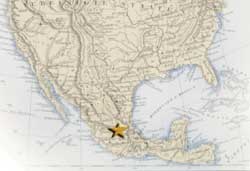 First ISO 9001:2000 Registration Achieved in Latin America First ISO 9001:2000 Registration Achieved in Latin America
T
he Department of Taxation for the City of Aguascalientes, Mexico, has achieved compliance to ISO 9001:2000. This marks the first registration to the standard in Latin America,
according to BSI, which issued the certificate of registration. "The citizens today demand a municipal government of high quality," notes Luis
Armando Reynoso Femat, mayor of Aguascalientes. "A quality management system defines and follows planned actions in a systematic way, thus generating
the appropriate level of trust within an organization and its customers." "Aguascalientes is a model for all to see," comments Ronald D. Mathis, vice
president of marketing and sales at BSI, who presented the certificate of registration. "The dedication and enthusiasm are infectious and the
improvements to the government through the morale of its people and the associated cost reductions are evident everywhere."
During an October celebration of the 426th anniversary of Aguascalientes, the city council organized a National Forum for Quality, drawing more than 800
officials from 150 Mexican cities. The forum focused on Aguascalientes' experiences and success with registration of its public service.
Aguascalientes' economic growth has reached 6.8 percent in the last five years, which is more than double the national average of 2.8 percent. Moreover, the
city has achieved significant results in the areas of urban infrastructure and services. For more information about the city, visit www.mexonline.com/aguacal.htm .
New Technology Detects
Flaws at the Atomic Level A
new development in nondestructive testing is capable of determining whether a material is flawed and, if not, when it will become flawed.
Positron Systems Inc. recently announced the availability of Photon Induced Positron Annihilation technology, which can precisely detect component fatigue
and embrittlement in bulk materials at the atomic level. Devices utilizing this technology can determine whether a material will become cracked or flawed
before any defect occurs. PIPA is also able to assess the remaining useful life of metallic, composite and polymer materials in a more precise manner than
radiography, eddy current, ultrasonic or other nondestructive evaluation methods. This advancement in nondestructive testing may help companies prevent
component failure because of fatigue cracks, allowing safe service life extension for expensive and critical parts, such as those used in aircraft, bridges and nuclear reactors.
The technology was invented by scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Idaho National Engineering and Environmental Laboratory. It has been licensed
to Positron Systems for commercial use. "Fatigue and embrittlement are multibillion-dollar problems that cause material
failures, downtime, premature replacement of expensive parts, and in some cases, loss of human life," says Steve Bolen, Positron Systems' CEO. "Early
detection of fatigue and embrittlement damage and identifying the remaining useful life of components will save money, increase safety and extend the
uninterrupted operation of critical parts such as those used in aircraft, nuclear reactors and power generation facilities."
The PIPA technology works by penetrating materials using a photon beam generated by a linear accelerator, which propels charged particles in a straight
path using alternating high-frequency voltages. This process creates positrons, which are attracted to nano-sized defects in the material. A positron is a
positively charged subatomic particle having the same mass and magnitude of charge as an electron. It constitutes the antiparticle of a negative electron. When
the positron collides with electrons in the material, the electrons are annihilated, releasing energy in the form of gamma rays. The gamma ray energy spectrum
creates a distinct and readable signature of the size, quantity and type of defects present in the material.
PIPA technology is available through Positron Systems' Lab Based Test and Analysis Center at Idaho State University in Pocatello, Idaho. Mobile systems
for deployment at customer sites will be available in the first half of this year. For more information, call (208) 672-1923. The Positron Systems Inc.
headquarters are located in Boise, Idaho. Visit the company's Web site at www.positronsystems.com.

Douglas R. Starrett 1920–2001
|
CEO of the L. S. Starrett Co. and one of Athol, Massachusetts,' most notable residents, Douglas R. Starrett died Nov. 5, 2001. He was 81 years old. Born April 2, 1920, in Framingham, Massachusetts, he was the son of Arthur H. and Ruth (Heinrich) Starrett, and lived in Athol all his life, graduating from
Athol High School in 1937. Starrett attended Worcester Academy and Dartmouth College. His great-grandfather, Laroy Sunderlin Starrett, founded the company in 1880.
A factor in shaping the community, the Starrett name can be found not only at the company sign, but also all over town--the Starrett Memorial Church,
Starrett Ave. and the Starrett building, for example. Although he was one link in a chain of executive Starretts at the company,
Douglas R. Starrett began his professional career the same way many young men in Athol did--by enrolling in a toolmaker's apprentice program. Shortly
thereafter, Starrett enlisted in the Army Air Corps during World War II. He served as a bomber pilot for three years with the 8th Air Force in the European
Theatre. After service, he went back to Athol to complete his toolmaker training. Known to many as a straightforward businessman, he worked his way to an
executive position at the company, first becoming an experimental toolmaker, then methods engineer, chief methods engineer, assistant vice president, vice
president in charge of plant operations, and executive vice president in 1956. In 1962 he became president of the company after the death of his father. During
his career, he was integral in establishing L.S. Starrett subsidiaries in Scotland and Brazil. Starrett was also known for his contributions to the Athol community. He was
president of Athol's YMCA for 30 years, making him the third of three Starretts to serve as YMCA president since 1850.
Starrett had recently handed the CEO baton over to his son, Douglas A. Starrett, who is also president of the company. Reports Show Past, Present
and Future of e-Learning A
s technology advances, in creeps a twinge of anxiety--the nightmare that someday you'll show up to work and notice that a computer is sitting where
your desk once did. The boss says, "Go home and don't worry about coming back." A worker that won't ask for days off has replaced you.
Fear not, trainers: According to Training magazine's 20th annual Industry Report, people still prefer to be taught by humans.
The report details the formal training activity of U.S. organizations with 100 or more employees. According to the study, despite predictions that online training
delivery methods will one day make classroom learning obsolete, 77 percent of all training is still conducted by an instructor in a classroom--a 4 percent
increase from last year. Computer-based and instructor-led training from remote locations dropped by 2 and 1 percent, respectively.
The report also states that organizations spent nearly $57 billion on formal training activities in 2001, up from $54 billion spent in 2000. According to the
report, this increase in spending stems primarily from the increased salaries for training staff, which account for 66 percent of organizations' training budgets.
Outside expenditures (e.g., customized and off-the-shelf materials, seminars and conferences) remained steady at more than $19 billion. Training editors
project that, in response to the economic downturn, more than 15 percent of companies could see a decrease in 2002 training budgets.
Thirty-seven percent of all employer-sponsored training in the United States today is devoted to teaching computer skills, which remains the most popular
topic to teach via computer-delivered means and makes up 53 percent of such courses. CD-ROM remains the medium of choice for computer-delivered training.
Perhaps surprisingly, traditional classroom training is as popular a method for teaching computer skills as it is for teaching other subjects. Seventy-four
percent (up 2 percent from last year) of all IT training is delivered in classrooms by live instructors. However, trainees are 7 percent more likely to learn
computer skills through computer-based training programs than other topics taught solely by computers.
Although Training's study shows strong support for human-led training, Online Learning Magazine reported a rise in the popularity of e-learning. The
magazine's October 2001 State-of-the-Industry Report shows that more than 80 percent of survey respondents are using some form of e-learning, specifically
online courses. Of those who implement e-learning in the workplace, 82 percent say they are happy with the results.
Online learning is a fairly new medium for employee training, according to the report. Overall, 27 percent of those who responded said their company has
been using e-learning for one to two years, and 25 percent said their company began this type of training less than a year ago.
The survey also delved into questions about why companies have avoided implementing e-learning for employees. Of the responses, 44 percent said
budget restraints have prevented the use of e-learning; 43 percent cited a lack of management buy-in; 19 percent reported that employees are not motivated
to learn online; and 15 percent indicated a lack of employee access to the Internet. Other factors include concerns about the quality of content, no time to
implement an e-learning program and a lack of knowledge or trust within the organization. For an abridged version of the 20th annual Industry Report, go to www.trainingmag.com . For the complete report, contact Training's circulation department at (800) 707-7760.
A copy of Online Learning Magazine's State-of-the-Industry Report can be found at www.onlinelearningmag.com. Guide for Metric System
Now Available in English T
he National Institute of Standards and Technology has made available a U.S. edition of the international standard reference guide to the International System
of Units (known as SI from the French Le Système International d'Unités), which outlines the modern metric system.
The International Systems of Units (SI) (NIST Special Publication 330) includes full technical definitions of official SI units, historical notes on the
development of present-day definitions and brief descriptions of some important units. In addition, the NIST version includes special notes concerning metric use in the United States.
The Omnibus Trade and Competitiveness Act of 1988 designates the metric system of measurement as the preferred system of weights and measures for
U.S. trade and commerce. The new NIST guide reflects the most recent interpretations of SI for the United States by the Secretary of Commerce as
published in the Federal Register of July 1998. The Secretary of Commerce has granted NIST the authority to interpret or modify the SI for
U.S. use. NIST coordinates federal government policy on the conversion to SI by federal agencies, and on the use of SI by U.S. industry.
The guide is an English version of an edition published by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures. It is available online at
physics.nist.gov/Pubs/SP330/sp330.pdf or by e-mailing a request to metric_pgr@nist.gov .
Industry News
Aon Launches Organization to Assist Company Improvement
 Aon Corp. has launched Management Consulting, an organization designed to help companies improve productivity, efficiency, bottom-line growth and organizational leadership.
Aon Corp. has launched Management Consulting, an organization designed to help companies improve productivity, efficiency, bottom-line growth and organizational leadership.
Aon Management Consulting will deliver the Rath & Strong Six Sigma suite of quality management services and offer service in the areas of employee
assessment and selection, leadership and organization effectiveness. Former head of Aon Consulting Rath & Strong, Daniel L. Quinn, will serve as president
of the organization. For more information, visit www.aon.com .
ASQ Offers Two New e-Learning Courses
The American Society for Quality is now offering Online Six Sigma Black Belt
Certification Review and Online Six Sigma Green Belt, two new courses available at the ASQ e-Learning Center at www.asq.org/ed/e-learn/ .  The Black Belt certification training offers the
define-measure-analyze-improve-control methodology presented with case studies and examples drawn from service, business process and manufacturing applications. The course length is 120 hours. The Black Belt certification training offers the
define-measure-analyze-improve-control methodology presented with case studies and examples drawn from service, business process and manufacturing applications. The course length is 120 hours. The online Green Belt course consists of 60 hours of training in lean manufacturing, system dynamics concepts and Six Sigma. Brown & Sharpe Acquires D&R Services
Brown & Sharpe Inc. has acquired D&R Services, a York, South
Carolina-based precision measurement service, calibration and repair company.
D&R Services will join the recently acquired Meas Inc. to effectively reestablish the Brown & Sharpe Precision Center in Charlotte, North
Carolina. The Charlotte facility will offer applications engineering and aftermarket services, including contract inspection and part programming and software training to
customers in the Southeastern United States. Learn more at www.brownandsharpe.com . TÜV Product Service Introduces
Health Care Web Site
 The Medical, Health and Sports division of TÜV Product Service has developed www.iso9000healthcare.com , a Web site
designed specifically for the health care industry. The site promotes and facilitates improved patient safety, economic effectiveness and provider/consumer morale. Focused on offering
health care providers information on developing practices in management, the site explains the relationships among ISO 9000, Six Sigma process improvement and Baldrige criteria. The Medical, Health and Sports division of TÜV Product Service has developed www.iso9000healthcare.com , a Web site
designed specifically for the health care industry. The site promotes and facilitates improved patient safety, economic effectiveness and provider/consumer morale. Focused on offering
health care providers information on developing practices in management, the site explains the relationships among ISO 9000, Six Sigma process improvement and Baldrige criteria.
The site also provides links to other health care sites, published articles by health care experts, an "Ask the Experts" section and a list of TÜV partners. |