ISO Survey Reports Registration
Growth
With the deadline to transition
looming and a number of surveys indicating that organizations
won’t transition in time, the state of ISO 9001:2000
registration is largely a matter of speculation. To gain
a sense of registration growth, the International Organization
for Standardization has conduced its 12th cycle of The ISO
Survey.
A total of 611,209 management systems had been registered
to ISO 9000 or ISO 14000 standards at the end of 2002, compared
to 547,381 the previous year, according to the survey.
The 12th cycle reports the following highlights:
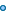 Through the end of December 2002, 561,747 ISO 9000 certificates
had been issued, compared to 510,616 certificates through
December 2001.
Through the end of December 2002, 561,747 ISO 9000 certificates
had been issued, compared to 510,616 certificates through
December 2001.
 The top 10 countries for growth in ISO 9000 certificates
in 2002 were China (+17,972), Italy (+13,103), Spain (+10,941),
Japan (+6,579), Hungary (+2,892), the Czech Republic (+2,862),
India (+2,566), the United States (+1,901), Singapore (+1,866)
and Switzerland (+1,694).
The top 10 countries for growth in ISO 9000 certificates
in 2002 were China (+17,972), Italy (+13,103), Spain (+10,941),
Japan (+6,579), Hungary (+2,892), the Czech Republic (+2,862),
India (+2,566), the United States (+1,901), Singapore (+1,866)
and Switzerland (+1,694).
 The number of registrations to ISO 9001:2000 more than tripled
in 2002.
The number of registrations to ISO 9001:2000 more than tripled
in 2002.
 The top 10 countries for ISO 9001:
The top 10 countries for ISO 9001:
2000 registrations at the end of 2002 were China (40,997),
Japan (16,813), Italy (14,733), Germany (10,811), the United
Kingdom (9,301), Spain (8,872), Australia (7,024), France
(6,529), Switzerland (5,060) and the United States (4,587).
 By the end of 2002, at least 42,462 ISO 14001 registrations
had been issued in 118 countries, an increase of 12,697
since the end of 2001.
By the end of 2002, at least 42,462 ISO 14001 registrations
had been issued in 118 countries, an increase of 12,697
since the end of 2001.
 Top 10 countries for growth in ISO 14001 registration were
Japan (+2,497), China (+1,718), Spain (+1,164), the United
States (+975), Sweden (+660), Brazil (+550), France (+375),
Germany (+320) and Hungary (+300).
Top 10 countries for growth in ISO 14001 registration were
Japan (+2,497), China (+1,718), Spain (+1,164), the United
States (+975), Sweden (+660), Brazil (+550), France (+375),
Germany (+320) and Hungary (+300).
“Growth can fluctuate from one year to another,
and it would be superficial to [evaluate] the success of
ISO 9000 and ISO 14000 solely in terms of the number of
registrations,” says ISO Secretary-General Alan Bryden.
“At a time when the globalization of many issues opens
world markets, ISO’s management system standards provide
a globally understood framework for business and thus contribute
to creating an upgraded and level playing field.”
The ISO Survey includes data on the following aspects
of both ISO 9000 and ISO 14001:
 World, regional and country-by-country totals of certificates
World, regional and country-by-country totals of certificates
 A breakdown of the world total by industrial sector
A breakdown of the world total by industrial sector
 A breakdown by country of withdrawn certificates of registration
A breakdown by country of withdrawn certificates of registration
 In the case of ISO 9001:2000, an indication of whether the
registrations represent new users or migrations from the
1994 versions of ISO 9001, 9002 and 9003
In the case of ISO 9001:2000, an indication of whether the
registrations represent new users or migrations from the
1994 versions of ISO 9001, 9002 and 9003
 Whether ISO 9001:2000 certificates cover single or multiple
sites, and whether the certificates are accredited or nonaccredited
Whether ISO 9001:2000 certificates cover single or multiple
sites, and whether the certificates are accredited or nonaccredited
The ISO Survey of ISO 9000 and ISO 14001 Certificates
is available as a combined 42-page report and CD-ROM. An
abridged version is posted online at www.iso.org.
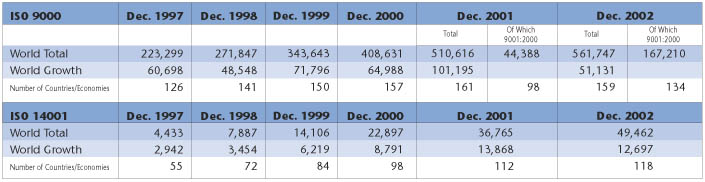
Count Down to ISO 9001:2000 Transition
New Standard Targets Project Management
Excellence
A new standard in the ISO 9000
family provides guidelines for quality management of projects,
wherever they’re carried out and whatever the type
or size of the organization.
Published by the International Organization for Standardization,
ISO 10006:2003, Quality Management Systems--Guidelines for
quality management in projects, offers a structured approach
for the optimal management of all processes involved in
any project, including those that cut across both the internal
and external boundaries of the organization.
Using the standard, organizations can ensure that they’re
applying a process-based approach to projects, in accordance
with ISO 9001:2000. Although not a requirement of ISO 9001,
ISO 10006 can be used as a basis for agreement among organizations
involved in a common project.
“The creation and maintenance of process and product
quality in a project requires a systematic approach,”
says Reg Sutcliffe, principal U.K. expert to the working
group that developed the standard. “ISO 10006 provides
an approach aimed at ensuring that the customer’s
stated and implied needs are met, that other interested
parties’ needs are evaluated and that the organization’s
quality policies are taken into account in the management
project.”
The new standard outlines principles and practices applicable
to projects of varying complexity, size and duration. It
allows organizations to monitor and realize objectives not
only of the project process but also of the project product
itself, therefore achieving quality in both.
ISO 10006:2003 is the work of ISO Technical Committee
176 Subcommittee SC2. A copy of the standard is available
from ISO national member institutes, a list of which can
be found at www.iso.org.
ANSI Approves Three Radio Frequency Communications
Standards
The International Committee
for Information Technology Standards has approved three
new standards that define two air-interface protocols and
a single application programming interface for real-time
locating systems used in asset management. The standards
relate to radio band frequency for communication within
an organization.
INCITS Technical T20 developed the three INCITS 371 standards
over a two-year period. The American National Standards
Institute and the INCITS’s executive board both approved
the series.
“Everyone on the technical committee recognized
the huge business value of establishing standards for RTLS
technology,” says Larry Graham, global manager of
manufacturing technologies at General Motors Corp. and chairman
of T20. “This standard will encourage widespread adoption
of wireless location systems--as the technology has already
proven to deliver tremendous bottom-line savings for enterprises
around the world.”
The INCITS 371 series includes:
 INCITS 371.1:2003, Information Technology--Real Time Locating
Systems (RTLS), Part 1: 2.4 GHz Air Interface Protocol.
This document establishes a technical standard for radio
frequency beacon systems that operate at an internationally
available 2.4 GHz band frequency. The standard is suitable
for applications in which assets need to be tracked throughout
extensive areas that are within range of a permanent reader
infrastructure. A typical application might involve the
monitoring of vehicles through a multi-station assembly
line or within a delivery yard.
INCITS 371.1:2003, Information Technology--Real Time Locating
Systems (RTLS), Part 1: 2.4 GHz Air Interface Protocol.
This document establishes a technical standard for radio
frequency beacon systems that operate at an internationally
available 2.4 GHz band frequency. The standard is suitable
for applications in which assets need to be tracked throughout
extensive areas that are within range of a permanent reader
infrastructure. A typical application might involve the
monitoring of vehicles through a multi-station assembly
line or within a delivery yard.
 INCITS 371.2:2003, Information Technology--Real Time Locating
Systems (RTLS), Part 2: Application Programming Interface.
This document establishes a technical standard for radio
frequency beacon systems that operate at an internationally
available 433 Hz band frequency and are intended to provide
presence and location data for assets that have fixed RTLS
tags. The standard is generally applicable for assets that
need to be tracked through zones within range of a permanent
reader infrastructure. A typical application might involve
the monitoring of mobile assets within a military installation.
INCITS 371.2:2003, Information Technology--Real Time Locating
Systems (RTLS), Part 2: Application Programming Interface.
This document establishes a technical standard for radio
frequency beacon systems that operate at an internationally
available 433 Hz band frequency and are intended to provide
presence and location data for assets that have fixed RTLS
tags. The standard is generally applicable for assets that
need to be tracked through zones within range of a permanent
reader infrastructure. A typical application might involve
the monitoring of mobile assets within a military installation.
 INCITS 371.3:2003, Information Technology--Real Time Systems
(RTLS), Part 3: Application Programming Interface. This
document defines the application programming interface.
To be fully compliant with this standard, RTLS must comply
with either Part 1 or Part 2. An API is a boundary across
which application software uses programming language to
invoke services.
INCITS 371.3:2003, Information Technology--Real Time Systems
(RTLS), Part 3: Application Programming Interface. This
document defines the application programming interface.
To be fully compliant with this standard, RTLS must comply
with either Part 1 or Part 2. An API is a boundary across
which application software uses programming language to
invoke services.
INCITS focuses on standardization in information and communications
technology, encompassing storage, processing, transfer,
display, management, organization and retrieval of information.
To learn more, visit www.incits.org.
 Book
Offers Eight Steps to a Lean Office Book
Offers Eight Steps to a Lean Office
Administrative functions represent
60 to 80 percent of the total cost of doing business. By
eliminating waste from these functions, a company’s
profit margin can increase. An important part of achieving
bottom-line savings is not only converting the factory floor
but also the office into a lean enterprise.
A recent book, Value Stream Management for the Lean Office:
Eight Steps to Planning, Mapping and Sustaining Lean Improvements
in Administrative Areas (Productivity Press, 2002) offers
executives, managers, supervisors and team leaders a complete
system for lean implementation in the office.
Authors Don Tapping and Tom Shuker modified their factory-floor
lean transformation process presented in their first book
Value Stream Management and adapted it to work in the office.
This how-to book discusses lean tools such as 5S, continuous
flow, kanban and standardized work.
The eight steps discussed in the book are:
1. Commit to lean
2. Choose the value stream
3. Learn about lean
4. Map the current state
5. Identify lean metrics
6. Map the future state--customer demand, continuous flow
and leveling
7. Create kaizen plans
8. Implement kaizen plans
The book also includes a complete case study that illustrates
the applications of lean in an office environment; an overview
of basic lean concepts; methods for identifying the administrative
activities that need improvement; guidelines and checklists
to help direct and maintain lean improvements; definitions
of common lean terms and concepts; and a CD-ROM containing
lean assessment tools, a storyboard template, charts, a
team charter, forms, reports and worksheets.
To learn more, visit Productivity Press at www.productivitypress.com.
 Benchmark
Study Lends Human Resources Advice Benchmark
Study Lends Human Resources Advice
Leading companies understand
that one of their most valuable resources is their employees.
In turn, human resource managers integrate employee appraisal
into HR training to generate the most effective performance
management and development processes, according to a study
from research and consulting firm Best Practices LLC.
“Best Practices in Employee Performance Management
and Development” shows how training practices have
proven profitable. Some examples include:
 One benchmark partner developed an apprenticeship program
to develop employee knowledge across skill competencies.
The program enabled the company to achieve Six Sigma production
quality and a 90-percent retention rate of employees who
participated in the program.
One benchmark partner developed an apprenticeship program
to develop employee knowledge across skill competencies.
The program enabled the company to achieve Six Sigma production
quality and a 90-percent retention rate of employees who
participated in the program.
 One manufacturer that participated in the study requires
that 85 percent of its employees be in continuous training.
The company’s production rates are four times faster
than that of its competitors. The company attributes this
growth to continual employee training.
One manufacturer that participated in the study requires
that 85 percent of its employees be in continuous training.
The company’s production rates are four times faster
than that of its competitors. The company attributes this
growth to continual employee training.
 A benchmark partner put continuous training first among
its priorities and allowed its training budget to make up
3.3 percent of its annual payroll. This allows the company
to generate customer price reductions of up to 22 percent.
A benchmark partner put continuous training first among
its priorities and allowed its training budget to make up
3.3 percent of its annual payroll. This allows the company
to generate customer price reductions of up to 22 percent.
Based on information gathered from 70 companies in more
than 30 industries, the study contains best practices, benchmarking
metrics, case studies and lessons learned. It also contains
recruiting and career planning strategies, training information,
cost and time investment, delivery methods, and employee
evaluation rating systems.
“World-class companies are making tremendous improvements
in all areas of human resources,” says Chris Bogan,
president and CEO of Best Practices. “These companies
are investing billions of dollars to develop systems that
will increase employee retention and overall workforce morale.”
To download a summary of the study, visit www3.best-in-class.com/rr156.htm.
INDUSTRY NEWS
Instantis has partnered with
George Group to develop software solutions for lean Six
Sigma project selection and tracking, knowledge management,
and effective reporting.
George Group, creator of the first lean Six Sigma process,
has expertise in program design and a curriculum for lean
Six Sigma, design for lean Six Sigma, leadership and lean
masters. For more information, visit www.instantis.com/sixsigma.
Veeco Instruments Inc. has
purchased the atomic force probe business of NanoDevices
Inc.
“This strategic technology will help Veeco provide
its customers with probes designed specifically to maximize
the performance of Veeco’s atomic-force microscopes
and will accelerate our development of new AFM products
where innovative probe technology can be the critical element,”
says Don Kania, president of Veeco. For more information
about Veeco Instruments, visit www.veeco.com.
The Pratt & Whitney Metrology
business unit of Siemens Measurement Systems has been divested
from Siemens Energy and Automation. The new company will
now be known as Pratt & Whitney Measurement Systems
Inc.
Pratt & Whitney designs, manufactures and services
length metrology instruments for use in calibration laboratories.
Pratt & Whitney applications include SuperMicrometer,
LabMaster, Laseruler, LabMicrometer, Electrolimit and GageCal.
For more information, visit www.prattandwhitney.com.
Entela-Boston needed more room
after expanding its testing capabilities and adding new
equipment. Consequently, the company has relocated to a
new facility that is more than 50-percent larger than its
original location.
Entela’s new equipment includes an Unholtz-Dickie
vibration machine, a Cincinnati subzero AGREE chamber and
a five-meter EMC chamber. With the addition of the new equipment,
Entela-Boston now offers the following performance tests:
vibration (sine, random and shock), thermal aging, thermal
cycling, programmable chamber exposures, temperature/humidity
and extensive EMC testing. For more information about Entela,
visit www.entela.com.
Perceptron’s laser scanning
Contour Probe will be used by Romer CimCore in a new scanning
inspection system that provides real-time analysis.
The system combines Perceptron’s Contour Probe laser
scanner, CimCore’s six- or seven-axis portable CMM
and Delcam’s PowerINSPECT software with embedded Perceptron
ScanWorks algorithms. The combination of the different technologies
provides real-time geometric and surface comparison to a
CAD file, point-cloud generation and output to additional
CAD applications. For more information about Perceptron,
visit www.perceptron.com.
Beta LaserMike has acquired
TSI Inc.’s length, speed and diameter product lines,
including the Holix series laser gages and the LaserSpeed
speed and length indicator.
“This acquisition not only expands our current product
offering, but it also expands our capabilities within existing
and new markets,” says Dan Doster, president of Beta
LaserMike.
TSI’s sales and service personnel will be retained
under the acquisition, and Beta LaserMike will continue
to support TSI’s current line of process instrument
products. For more information about Beta LaserMike, visit
www.betalasermike.com.
X-Rite Inc., a maker of precision
measurement devices, software and services, has acquired
Monaco Systems, a developer and distributor of color management
software to the graphic arts and photo markets.
The $10.6 million asset purchase is part of X-Rite’s
drive to offer color management solutions combined with
the company’s instruments.
This is the third color-management company acquisition
for X-Rite in 2003. Earlier this year, the company acquired
Benjamin Moore & Co.’s ColoRx product line and
related assets from Thermo Electron Corp., Benjamin Moore’s
former supplier. More recently, X-Rite acquired ccDot meter
products from Centurfax Ltd., a developer of prepress and
printing products. For details, visit www.xrite.com.
|